Track KPIs for a Clear View of Business Performance
Monitor Key Metrics and Understand Current Performance Trends
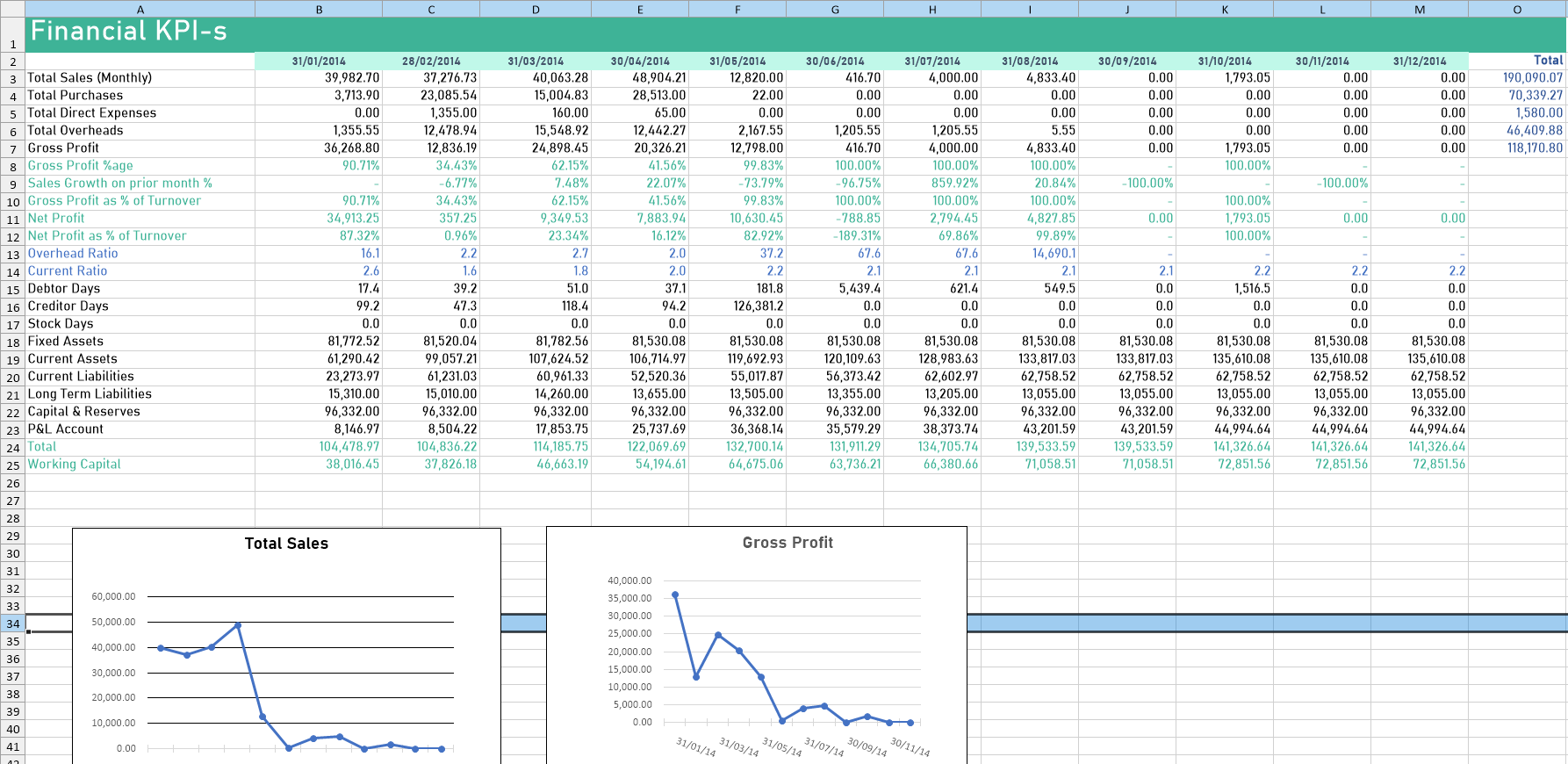
Calculate business performance KPIs.
-
Analyse summary data - Total Sales, Sales Growth, Gross Profit
-
Deliver most important ratios for the business
-
Export to Excel
- Total Sales (month)
- Sales Growth on prior month%
- Gross Profit
- Gross Profit as % of Turnover
- Net Profit
- Net Profit as % of Turnover
- Quick Ratio
- Current Ratio
- Debtor Days
- Creditor Days
- Stock Days
- Working Capital
These four metrics show how effective a management team is in generating money, considering the expenses associated with producing their goods and services.
The gross profit is the absolute GBP amount of revenue that a company generates beyond its direct production costs. Gross Profit as % of Turnover shows the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold.
Knowing your company's gross profit might help you come up with ideas for how to lower your cost of goods sold or raise prices for your products.
Net Profit is the revenue of your company after deducting all operating expenditures and your cost of goods sold. You need to know your company's gross profit to determine net profit.
You can identify expense reductions if your net profit is significantly less than your gross profit.
And if your net profit is significantly lower than your gross profit, you can determine expense cuts.
The company's liquidity rises as the quick ratio does. If necessary, more assets can be quickly turned into cash. This is a good sign for investors and an even better sign for creditors, as it assures them that they will be repaid on time.
A very high ratio isn't always a good thing, though. It might imply that money has accumulated but isn't being invested, returned to investors, or used in any other useful ways.
The current ratio is used to measure a company’s ability to pay off short-term debt.
The current ratio, as opposed to the quick ratio, considers all assets, including inventory held by the company, which is more difficult to convert to cash during that fiscal year.
Creditor Days show the average number of days your business takes to pay suppliers.
If the days ratio is trending lower than the standard terms of trade, this may be a sign that suppliers are being paid too quickly, which lowers the amount of cash available to the company, or it may be because suppliers are receiving early settlement discounts.
Stock Days is the number of days on average that a business holds its stock.
It is significant because a company frequently has a sizeable sum of money invested in its stock. Financial issues can arise from having an excessive amount of the incorrect inventory items.